First Step in Infertility Treatment: Intrauterine Insemination
In couples who apply with infertility problem, insemination can be done as the first step after necessary examinations are made.
It is necessary to create some basic conditions here. The woman must have at least one tube open healthy and this condition must be determined in advance with medicated uterine film.
Technically, the previously prepared eggs are based on the principle of transferring the prepared sperm to the intrauterine tissue after cracking.
* Women under the age of 39
* If at least one tube is open
* If the sperm count is over 5 million
* If the infertility period is below 5 years
* If the ovarian reserve has not decreased, it is recommended to try 2-4 times as the first step in treatment.
In the first stage of treatment, ovulation needs to be activated. When self-insemination with egg follow-up, pregnancy rates are given around 5%. Therefore, even if it is performed only due to the male factor, ovulation induction is recommended. Oral medicines (clomiphene citrate or letrozole) can be used here, as well as subcutaneous or intramuscular gonadotropins. Oral medications are low in cost and especially letrozole can be preferred because it creates both a small number of eggs and has no negative effect on intrauterine tissue. It is possible that clomiphene citrate may not thicken the intrauterine tissue from time to time. Gonadotropins should be used at low doses and excessive egg formation should be prevented. A large number of egg formation and high costs cause gonadotropins to be used less in insemination. However, there are also publications indicating that the insemination success after ovulation induction applied under the skin with gonadotropins is higher.
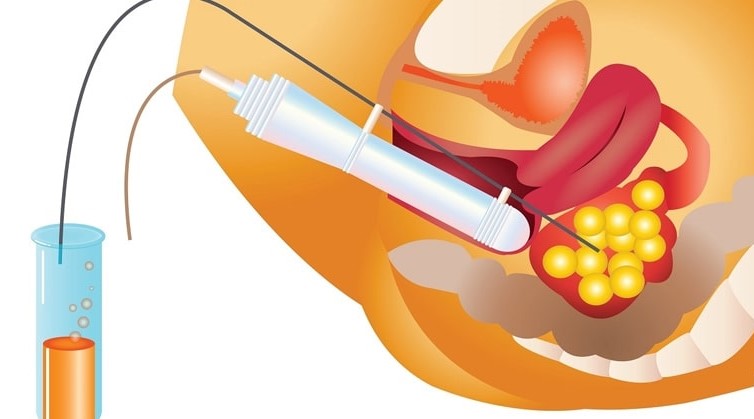
After the formation of the egg, the cracking needle is applied under the skin and 34-40 hours after the injection, the previously prepared sperm is given to the intrauterine tissue. The semen obtained by masturbation is prepared by a process that takes approximately 2 hours in the laboratory and the sperm, whose movement is increased and the density per volume increases, is gradually given to the intrauterine tissue in a small volume.
In insemination, if the number of eggs is three or more, the risk of multiple pregnancies in triplets and above may increase and therefore insemination should not be performed and association should be prohibited. In this case, either the treatment is cancelled for that month or by returning to the IVF method, eggs are collected and embryos formed by applying microinjection can be transferred to one or two if there are indications.
Care should be taken to avoid infection in the vagina or cervix before insemination. The risk of pelvic infection due to insemination may appear as a treatment complication.
The success of insemination is given as 9-20% in many studies. 2-4 insemination can be done considering the age of the woman, the number of eggs and the duration of infertility. When insemination success cannot be achieved, the IVF method should be started without wasting time. We now know that the success of treatment after two inseminations does not exceed the chances of a natural pregnancy of the couple, and we must tell the couples very well. However, if the woman has to postpone IVF treatment due to basic health problems or social reasons, then it may be considered to complete 4 inseminations.






 Turkish
Turkish Deutsch
Deutsch
 Bu İçeriği Beğendim
Bu İçeriği Beğendim